Reding, peeling the skin on the legs, the appearance of cracks between the fingers, ulcers on the feet, a change in the condition of the nails: loss of the shine, the usual pink shadow, thickening of the plates - these and other signs indicate the development of a fungal infection. Every fifth inhabitant of the earth is sick with mycosis. Therefore, you need to know how the fungus looks on the legs and behaves, what causes lead to its appearance and how this unpleasant illness can be treated.
Reasons
In most cases, the infection of mycosis comes from one person to one person directly or through the surrounding objects. Favorable conditions for the reproduction of the mushroom are fever, humidity. After poor processing of manicure tools, disputes can also be maintained in a dried state.
The main reasons for the disease are:
- Lack of regular feet care.
- Accommodation with a person suffering from a mushroom.
- Use someone else's shoes, socks.
- Stop injuries.
- Visit "mushroom" world areas (beaches, bathrooms, pools).
- Inadequate processing of accessories for the pedicure.
- Wear tight shoes from synthetic materials.
- Professional harm (work under the conditions of high temperature and humidity).
- Shoot shoes in a shop without a sock or department.
Mushroom diseases in humans develop faster against the background of the functions of how the functioning and changes that lead to the oppression of immunity, local circulatory changes, the skin condition. The reasons from the body are as follows:
- Endocrine pathology (diabetes, obesity);
- Pregnancy;
- Immune deficiency;
- increased sweating;
- Foot diseases;
- Vascular disorders;
- Chronic skin diseases (eczema, psoriasis);
- Long -term absorption of drugs that suppress immunity (corticosteroids, cytostatics).
Types of pathogenic mushrooms
Mushrooms on the human body feed on proteins - keratin, elastin, collagen that they share with enzymes: keratinase. The localization of mycosis depends on the activity of keratinase and the ability to digest different types of keratin.
Mycoses on the legs cause the following types of mushrooms:
- Trichophyton rubrum-a-type of mushroom saprophytes that live in a keratized skin layer. Causes cutting lichen, damage to the epidermis, nails in 80 % of cases.
- Trichophyton mentaGraphytes causes stop epidermophytius.
- Trichophyton interdigital. The fungus causes dermatophytosis, onychomycosis on the legs.
- Mushrooms of the genus Candida influence the skin and nail plates with a strong decrease in immunity to the skin and nail plates with a severe decrease in immunity.
Mushroom skin lesions
From mycosis on the legs, the skin lesion during psoriasis (sometimes it is called dry mushroom) - red plaques with peel and a tendency to climb over the surface. Such elements can often be found on the knees and legs. This disease is not associated with a fungal infection.
The manifestations of the foot mushroom of the foot are divided into four main forms. The convention is in a combination of clinical signs and the possibility of a transition from one to the other.
The skin is suffered in interdigital rooms in intertriginoser form. The mushroom of the skin of the legs manifests itself in the form of itching, combustion and is accompanied by an unpleasant smell. The infection often affects the foot from the intervals between 3 and 4, 4 and 5 fingers. The skin becomes red and impregnated with moisture, wounds, crying areas between the fingers. These characters develop independently or against the background of an existing squamous epithelial form.
Note! For the typical intertriginous lesion, the binding of a secondary bacterial infection that worsens the disease is. Bacterial, mycotic eczema develops with the formation of a rash not only on the foot, inflammatory elements on the ankle and lower.
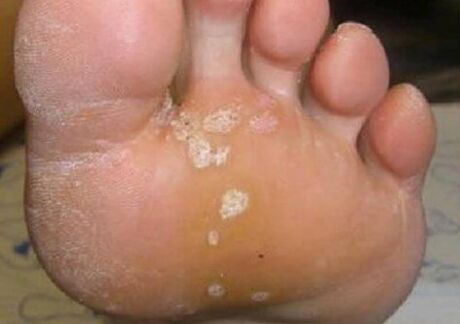
The advanced squamous hyperkeratotic form looks like usual massive grains on the sole with cracks. First of all, the mycosis of the skin of the legs with dryness, peeling the skin of the feet, the limited rough corn on the heels can attract. People consider such symptoms to be individual and do not turn to a dermatologist. Skin lesions can accompany itching and burning. If you look at the photos of the mushroom on the legs with this form of mycosis, you can determine deep cracks against the background of a thickened (so to speak in moccasins) of the skin of the feet. Such manifestations are painful. The squamous epithelium is characterized by the participation of nail plates with its destruction, a delay behind the nail bed.
The manifestations of the dyshidrotic (vesicular) form of the foot mushroom are rare. The main symptom of the disease is the formation of blisters with a thick shell and transparent content. They are localized on the sole side of the foot, the fingers as individual or drainage formations. Then the bubbles with purulent crusts around the edges are opened with the erosion formation. The complications of the vesicular lesion include:
- Toxic-allergic reactions. They develop for 4-6 days, often localized symmetrically: swelling reddish papules can be found on the foot, on the lower leg, on the forearm, on the face and on the mucous membrane.
- Connection of a secondary bacterial or viral infection with the development of eczema.
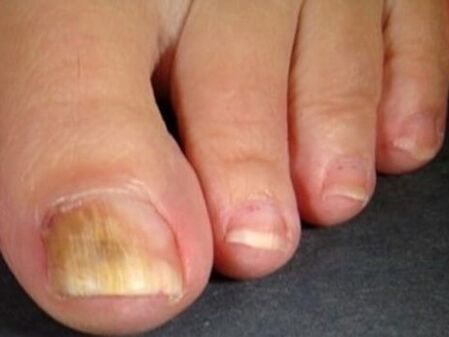
The deleted shape of the mushroom on the feet is characterized by minimal lesions, so it is not easy to see. The main signs: the appearance of board peeling, the formation of microricises between the fingers, symptoms, burn. The nail plates are involved with a long course.
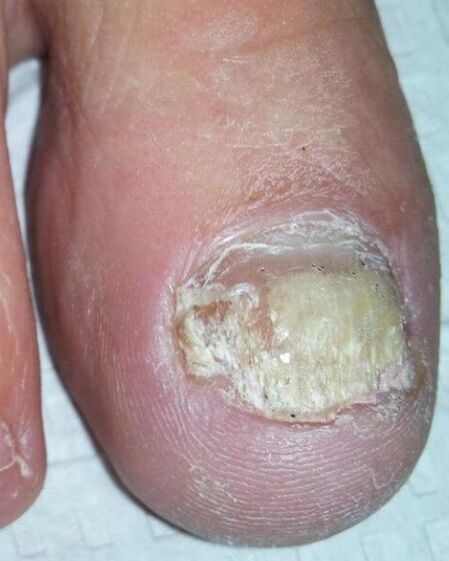
Nail fungus
Onychomycosis appears due to the skin mushroom on the fingers, feet, without attention to the problem and adequate treatment.
The first symptoms and signs of onychomycosis can also remain unnoticed. You should turn to the nail fungus on the legs and a dermatologist at:
- Change of the color of the nail plates;
- The appearance of yellow or gray spots;
- Loss of gloss;
- Appearance on the surface of the irregularities;
- Stripes in the structure of the nail;
- Increased brittleness.
There are different classifications of onychomycosis. Due to the appearance of the nail plate, they are divided into:
- Normotrophic. The fungal infection changes the color of the nails in yellowish-gray, the thickness and shape remain the same.
- Hypertrophic. This type of mushroom is characterized by rough changes: the nails are yellow, thicken. If you look at the photos that represent this type of onychomycosis, you can notice a characteristic correct form of the records. Cross studies, loosening and offenses in the free edge are visible. Such a change in nails leads to their growth. Walking will be painful.
- Onycholithic. The nail plates become thinner, change the color and peel out of the nail bed.
After localization and the degree of damage to the nail plate, the following types of onychomycosis are differentiated: distal; laterally; mixed, proximal; in total; Surface.
Candidiasis defeat
Regardless of this, the damage to the mushrooms of the genus Candida should be considered. These unconditional pathogenic fungi cause depth (effects on internal organs) and surface mycoses (dermatomycosis, onychomycosis). Under normal conditions, human immunity suppresses the reproduction of this fungus and there is no massive infection. Therefore, the activity of Candida manifests itself with considerable diseases in the body of the body's protection and requires a thorough examination to determine the cause of immune deficiency. The first signs of infection are difficult to distinguish frostbite.
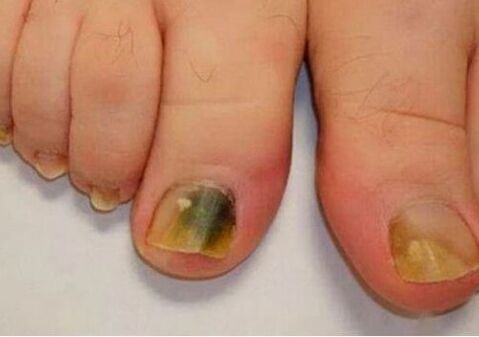
The mushroom damage on the legs develops as follows:
- On the fingers of the legs there is inflammation of the nail rollers with redness, swelling, cracked on the skin, the appearance of symptoms in all movements. Under the nail plates, a purulent separate, whitish shadow forms.
- Inflammatory changes in the skin examination, the disease becomes chronic. The skin around the nail thickens and no longer grows. The infection affects the nail plates.
- The nails on the legs begin to thicken, sprinkle. Their color becomes brown, brown. Violation of blood supply leads to rejection.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of the mushroom on the legs includes:
- Conversation with the patient (complaints, accompanying diseases, working conditions, clarification of the possibility of infection).
- Inspection.
- Laboratory research methods (scratches of the skin, nails with microscopy, sowing of a special harvest with the determination of sensitivity to medication, IG G over Aspergille, candidates).
Treatment
The fungus on the legs requires immediate treatment that a dermatologist (or mycologist) prescribes. You can do orders outpatient.
How and how to treat the mushroom on your legs depends on a series of conditions:
- Localization of the pathological process;
- Degree, severity of defeat;
- The presence of accompanying diseases;
- Patient age;
- In the case of therapy of women - the fact of pregnancy, breastfeeding.
The treatment of the mushroom on the legs takes a lot of time and its main goal is the disappearance of clinical and laboratory signs of an infection. An incomplete course of therapy leads to a relapse of the disease.
Pharmaceutical therapy
Medicine treatment is carried out with antifungals that not only destroy mycosis, but also help to eliminate the manifestations of inflammation and to eliminate the secondary infection.
You are divided into:
- Local. Apply to the lesion (ointment, gel, cream, spray, paint, solution).
- Systemic - take orally (tablets, capsules, solutions).
In the first phase of a fungal infection, drug therapy is limited to the appointment of local means. In the event of common mycosis, the connection is required with a difficult course of systemic antifungal.
Treatment with folk remedies.
There are many recommendations on how to get rid of the mushroom on the legs of folk and home remedies. Most implies external use and some inwards. However, you should not drink and apply dubious compositions to your feet to bring the neglected mycosis. Such folk methods can affect health.

Note! The most common and most effective home remedy for mushrooms are the legs for legs with salt, soda and essential oils. These therapeutic methods prepare feet and nails for the use of medicinal products.
Surgical treatment
The nail plates must be removed with solid mushroom damage. This method is safe and has practically no contraindications. An alternative to surgical manipulation - the use of pastes and ointments for softening nails, followed by distance.
Laser treatment
The use of a laser to combat onychomycosis is based on heating and destruction of the spores of the mushroom with a directed beam. This technique enables you to quickly heal onychomycosis, safe and applicable in patients who are contraindicated in systemic treatment.
Treatment of dermatomycosis
Local antifungals on the legs are used to start treatment of the mushroom. If there is no improvement in the disease after a two -week treatment, an antifungal agent is required. In the event of severe damage, the skin fungus requires the prescription of systemic drugs. The therapy continues until the infection is completely eliminated.
Treatment of onychomycosis
Local medication are prescribed to remove the initial manifestations of nail fungi. Mycosis with a lesion of more than 2/3 of the nail area, the growth zone, distribution to other plates - an indication of taking systemic medicines. Onychomycosis with massive destruction of the nail plates begins with the surgical removal of the nail affected. This method offers access to the focus of the infection.
Important!
The treatment of onychomycosis takes place before growing healthy nails and can take up to 12 months.
The appearance of the mushroom on the legs can be caused by various reasons. An attentive attitude to your health will help to recognize the disease in good time and to start treatment.